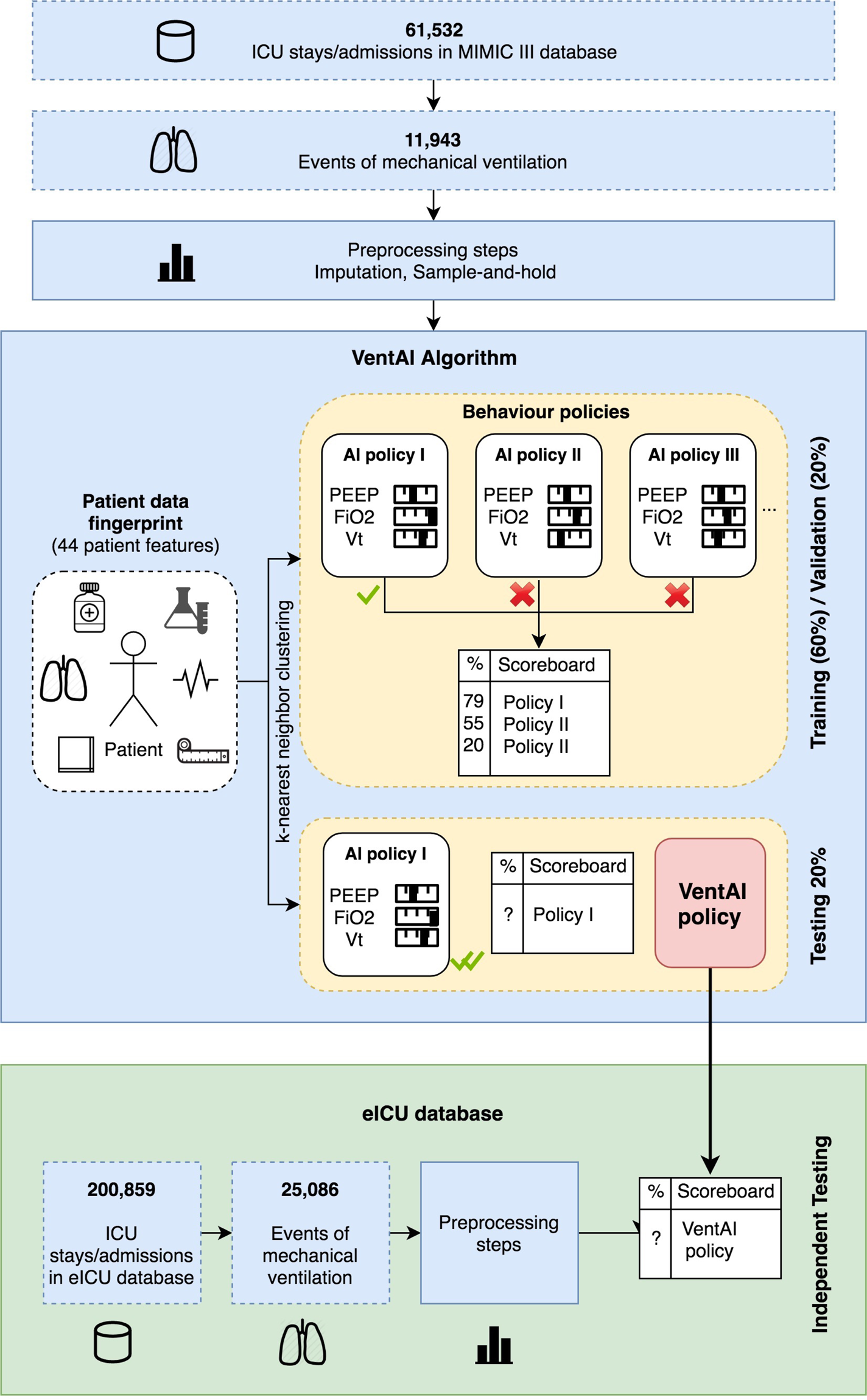
Development and validation of a reinforcement learning algorithm to dynamically optimize mechanical ventilation in critical care | npj Digital Medicine
Mechanical power of ventilation and driving pressure: two undervalued parameters for pre extracorporeal membrane oxygenation ventilation and during daily management? | Critical Care | Full Text
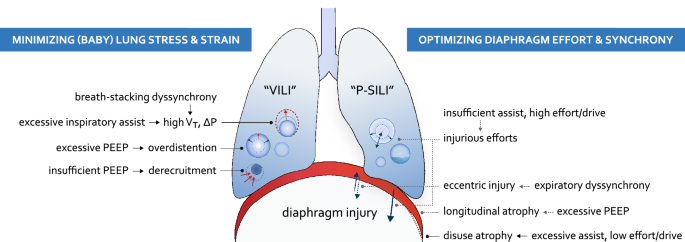
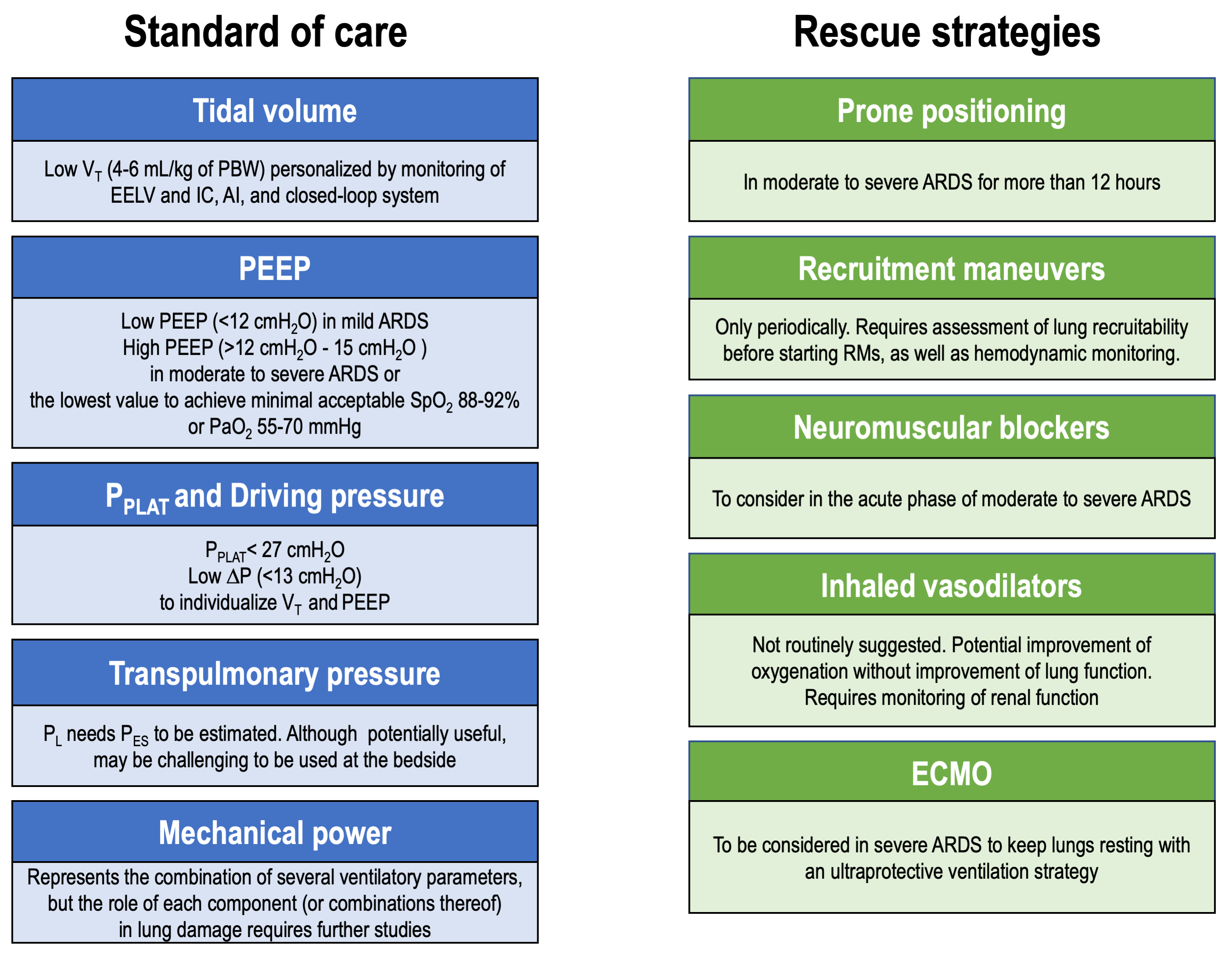
Clinical strategies for implementing lung and diaphragm-protective ventilation: avoiding insufficient and excessive effort | SpringerLink
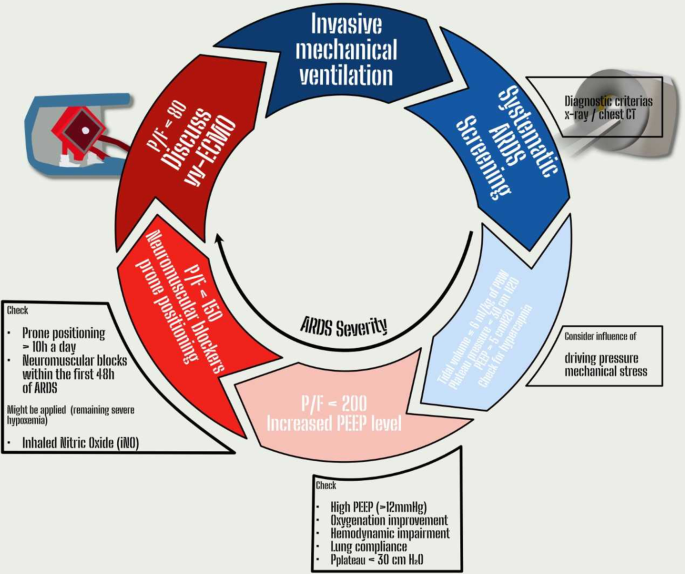
JCM | Free Full-Text | Mechanical Ventilation during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Narrative Review
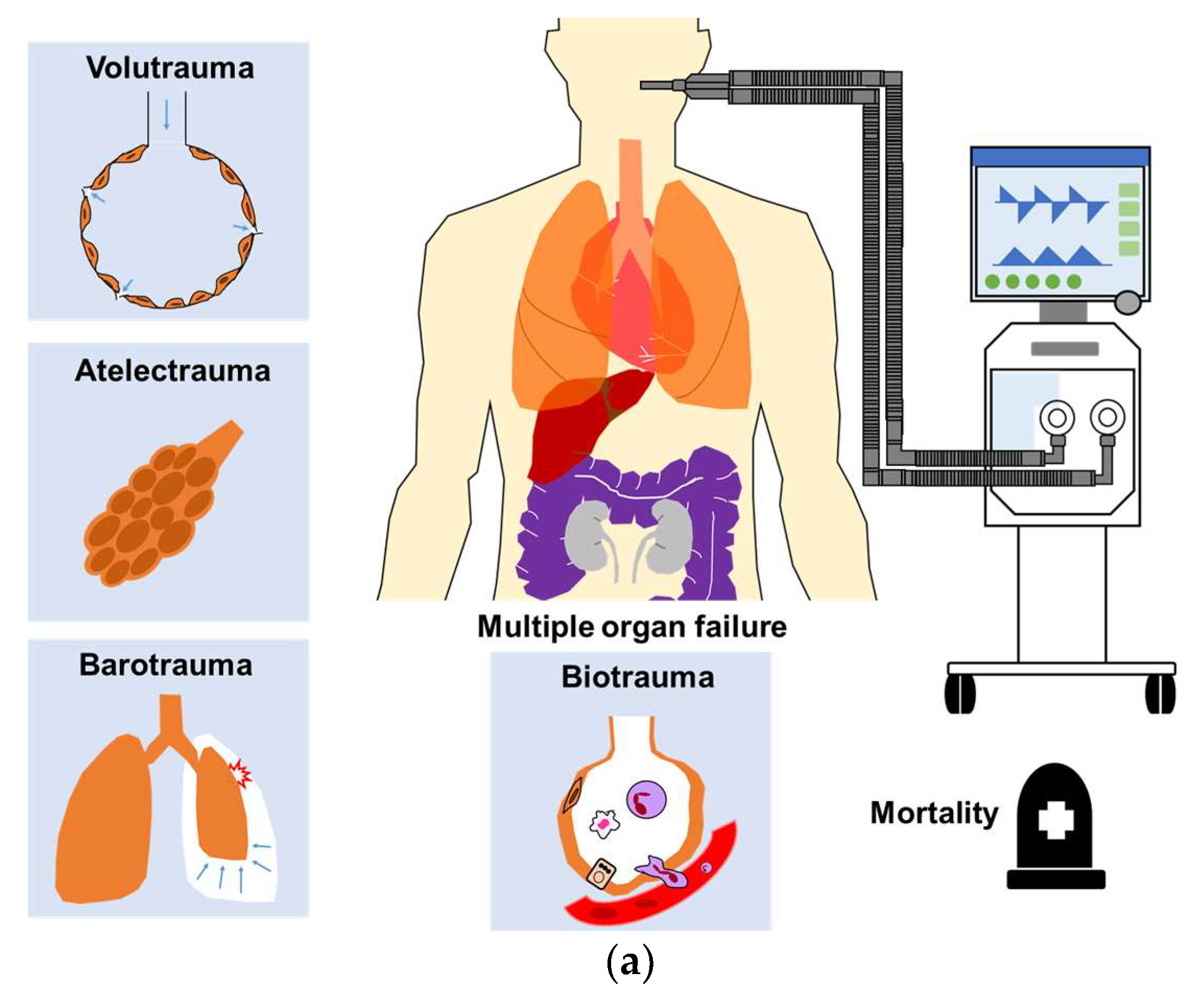
![PDF] Static and Dynamic Contributors to Ventilator-induced Lung Injury in Clinical Practice. Pressure, Energy, and Power | Semantic Scholar PDF] Static and Dynamic Contributors to Ventilator-induced Lung Injury in Clinical Practice. Pressure, Energy, and Power | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/78e7c86ffc24c49e5f3bbc32233634f31e1549cc/4-Figure2-1.png)
PDF] Static and Dynamic Contributors to Ventilator-induced Lung Injury in Clinical Practice. Pressure, Energy, and Power | Semantic Scholar

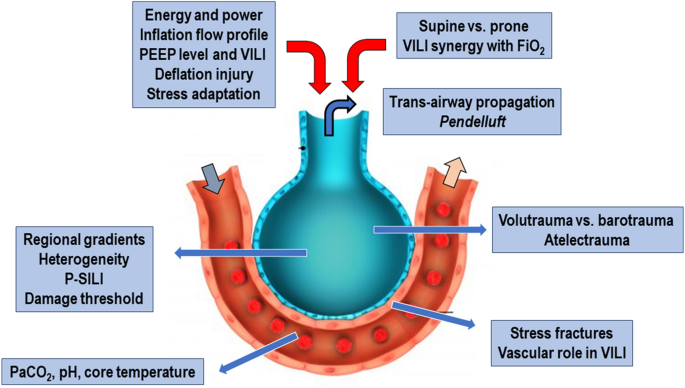
Lung stress, strain, and energy load: engineering concepts to understand the mechanism of ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) – topic of research paper in Medical engineering. Download scholarly article PDF and read for
Power to mechanical power to minimize ventilator-induced lung injury? | Intensive Care Medicine Experimental | Full Text
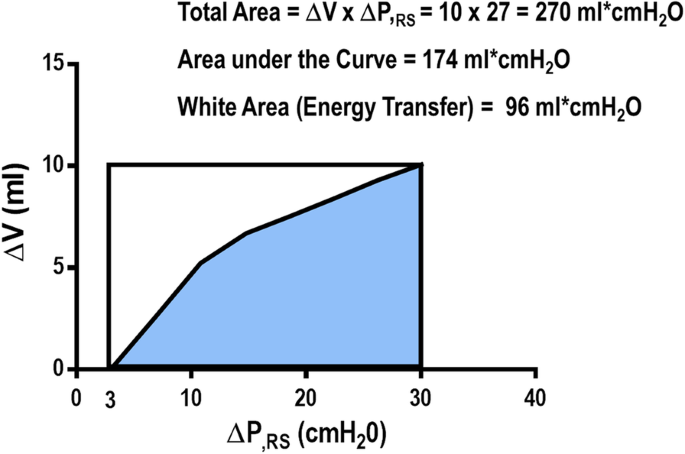
![PDF] Static and Dynamic Contributors to Ventilator-induced Lung Injury in Clinical Practice. Pressure, Energy, and Power | Semantic Scholar PDF] Static and Dynamic Contributors to Ventilator-induced Lung Injury in Clinical Practice. Pressure, Energy, and Power | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/78e7c86ffc24c49e5f3bbc32233634f31e1549cc/6-Figure6-1.png)
PDF] Static and Dynamic Contributors to Ventilator-induced Lung Injury in Clinical Practice. Pressure, Energy, and Power | Semantic Scholar
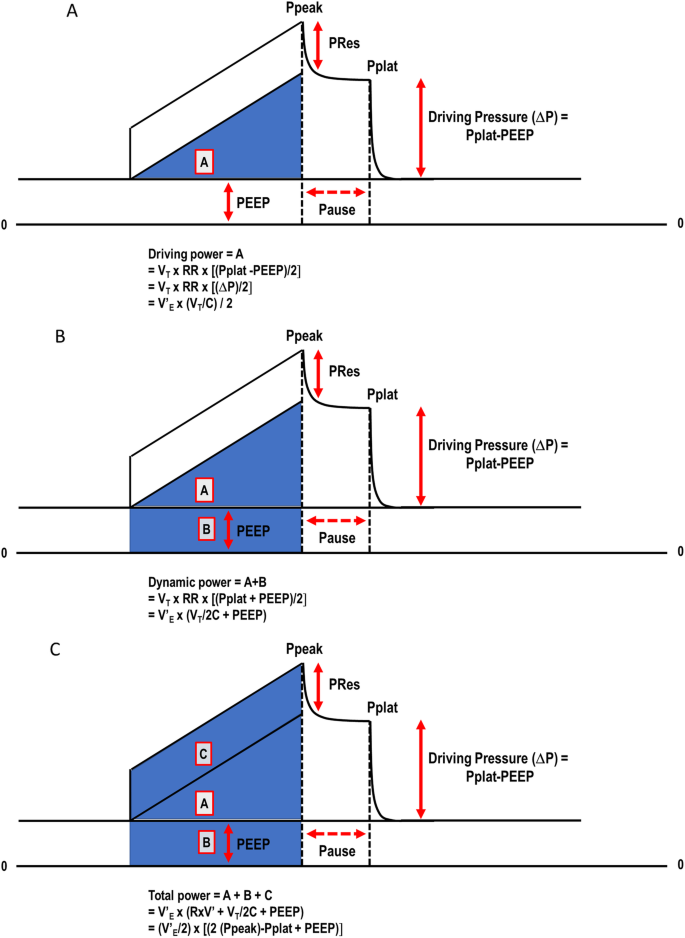
Elastic power but not driving power is the key promoter of ventilator-induced lung injury in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome | Critical Care | Full Text

Figure 3 from Driving pressure and mechanical power: new targets for VILI prevention. | Semantic Scholar
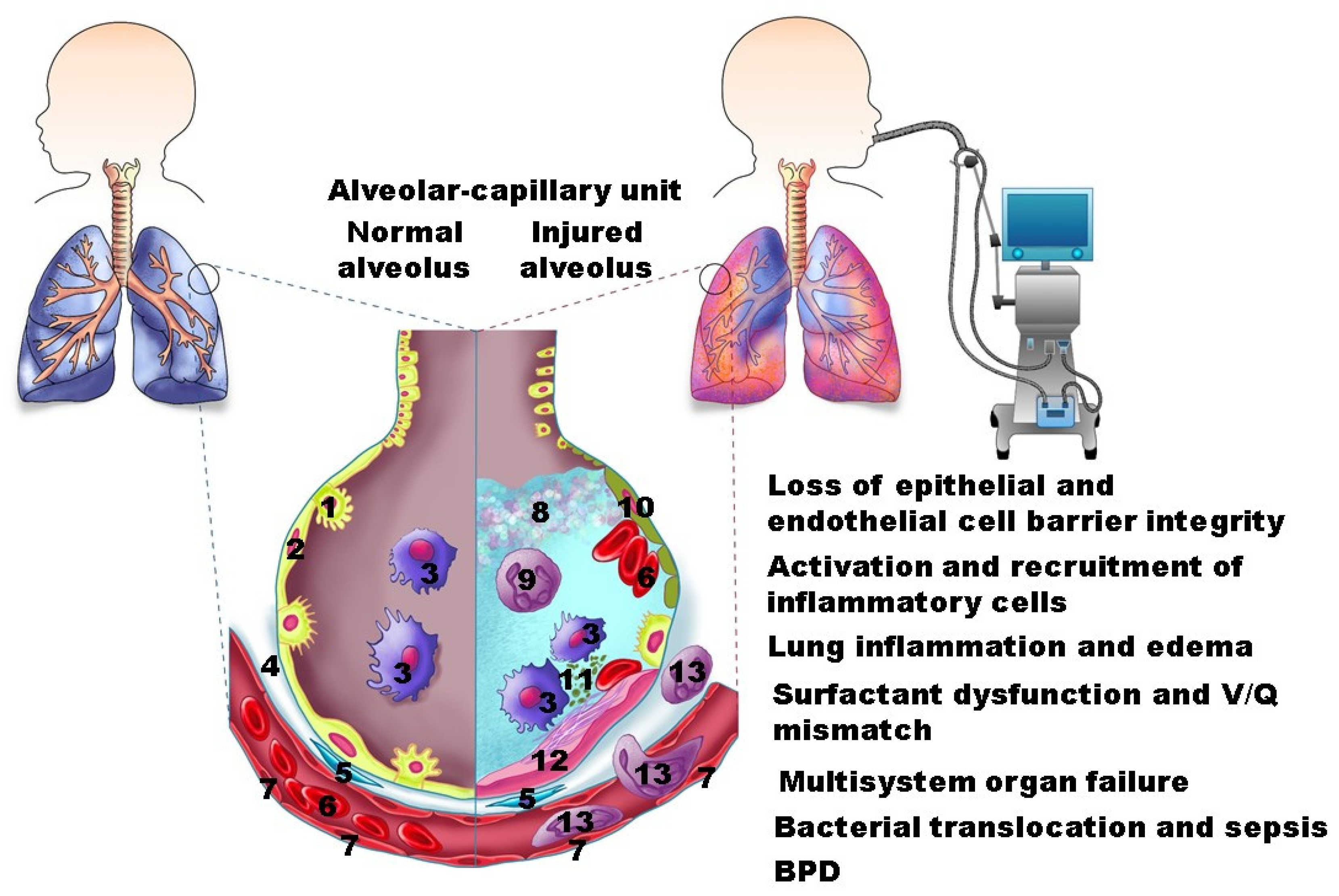
JCM | Free Full-Text | Ventilation-Induced Lung Injury (VILI) in Neonates: Evidence-Based Concepts and Lung-Protective Strategies

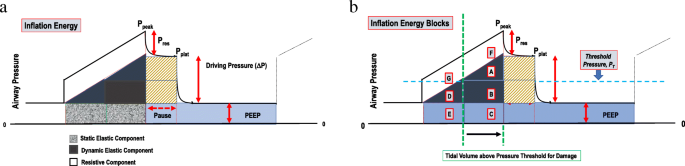
PDF) Risk factors of ventilator-induced lung injury: mechanical power as surrogate of energy dissipation

Power to mechanical power to minimize ventilator-induced lung injury? | Intensive Care Medicine Experimental | Full Text
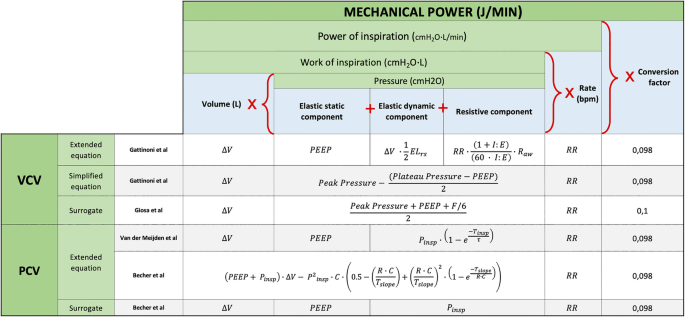
Mechanical power at a glance: a simple surrogate for volume-controlled ventilation | Intensive Care Medicine Experimental | Full Text
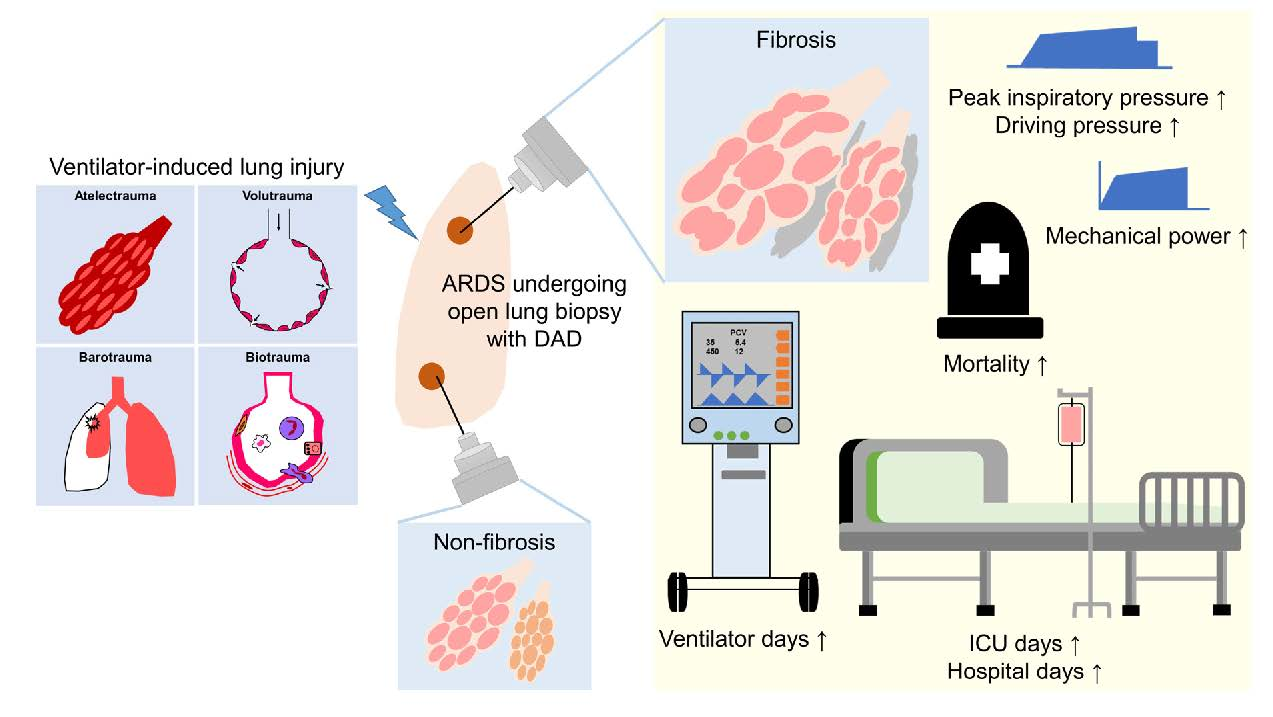
JPM | Free Full-Text | Relationship between Mechanical Ventilation and Histological Fibrosis in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Undergoing Open Lung Biopsy

Imaging atelectrauma in Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury using 4D X-ray microscopy | Scientific Reports
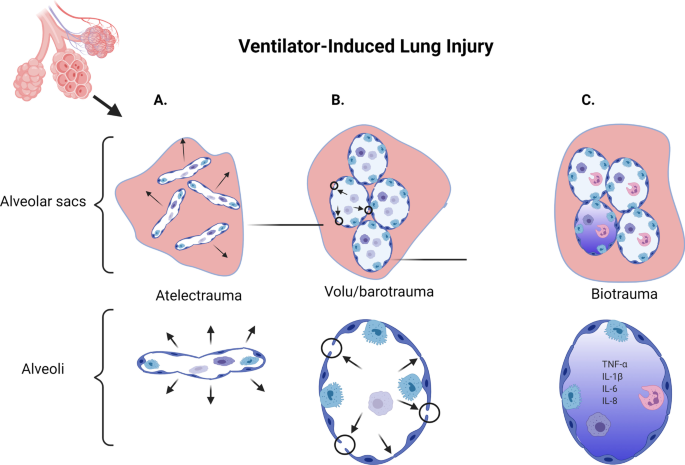
Ventilator-induced lung-injury in mouse models: Is there a trap? | Laboratory Animal Research | Full Text

Energy dissipation during expiration and ventilator-induced lung injury: an experimental animal study | Journal of Applied Physiology
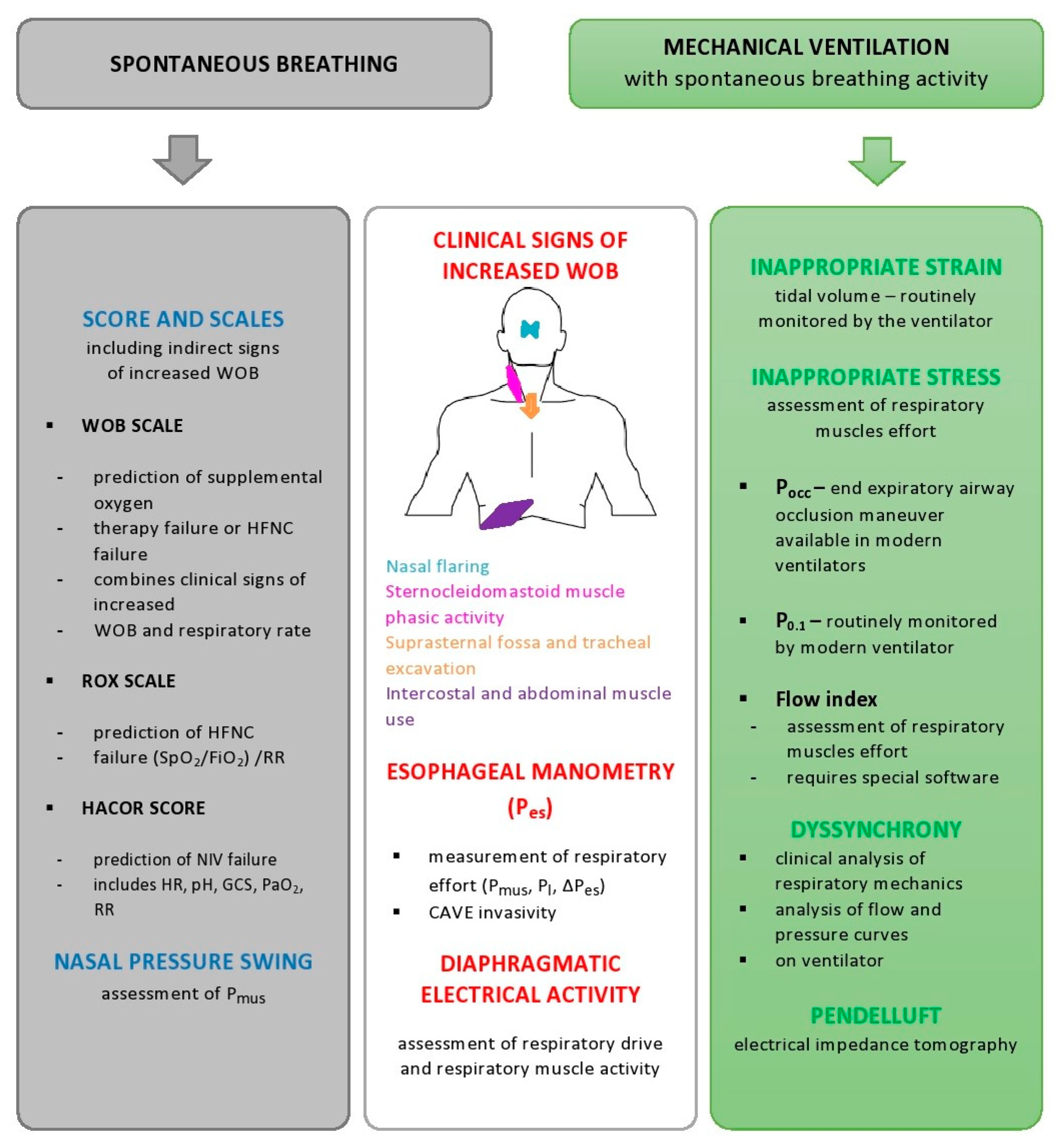
JPM | Free Full-Text | Patient Self-Inflicted Lung Injury—A Narrative Review of Pathophysiology, Early Recognition, and Management Options